What Does Grade 2 Diastolic Dysfunction Mean
What Does Grade I diastolic dysfunction mean in an individual. The first thing to recognize is that there is a high likelihood that your patient does not have Grade I diastolic dysfunction by current criteria.

Understanding The Basics Lv Filling Patterns
There may be left atrial enlargement due to elevated pressure in the left heart.

What does grade 2 diastolic dysfunction mean. Grade 2 diastolic dysfunction is rated as moderate heart failure. There may be left atrial enlargement due to elevated pressure in the left heart. EA 0815 DT 160200 milliseconds Ee.
Stage II suggests a decrease in left ventricular compliance especially when there is a large pulmonary vein a wave flow reversal. Whats Grade 2 Diastolic Dysfunction. Grade II diastolic dysfunction is called pseudonormal filling dynamics.
Diastolic dysfunction is described as grade 12 or 3 with 1 being mild and three being severe. Patients with normal diastolic function had lower EDVi20 than patients with Grade 3 diastolic dysfunction but there were no differences between patients with normal diastolic function and grade 1 of 2 diastolic dysfunction. Unfortunately studies have shown that no known medications improve diastolic heart failure.
DD is dangerous and is believed to be associated with congestive heart failure symptoms in patients who have whats called preserved left ventricular ejection fraction according to cardiologist Wael Jaber MD. Due to the high left ventricular pressures there is left atrial enlargement. This is also known as the pseudonormal filling dynamics.
When your heart isnt able to relax fast enough its called diastolic dysfunction DD. The grade 2 diastolic dysfunction is also known as the pseudonormal filling dynamics. Last week we reviewed some common errors found when measuring diastolic function.
This is considered moderate diastolic dysfunction and is associated with elevated left atrial filling pressures. This is considered moderate diastolic dysfunction and is associated with elevated left atrial filling pressures. The symptoms are quite similar to a cardiac failure.
Grade II This diastolic dysfunction is characterized by increased filling pressure in the atrium and is considered to be moderate stage disease. Diastolic dysfunction was diagnosed according to the echocardiographic examination results and categorized into 3 grades based on 2009 version of recommendations that is grade 1 mild diastolic dysfunction or impaired relaxation phase. It is a common finding with HCM which results from the hearts inability to properly relax due to the thickness and cellular structure.
Since the Intersocietal Accreditation Commission mandates both the assessment and reporting of diastolic function for echo accreditation we thought it would be a good idea to review these measurements again. This is diagnosed by echo. This week we will review 5 steps to identify diastolic dysfunction in echo.
These patients more commonly have symptoms of heart failure and many have left atrial enlargement due to the elevated pressures in the left heart. A major clue to the presence of grade II diastolic dysfunction as compared to normal diastolic function is the presence of structural heart disease such as left atrial enlargement left. Data are shown as median with error bars representing 25 and 75 percentile.
EA 200 milliseconds Ee 8 grade 2 moderate diastolic dysfunction or pseudonormal phase. The symptoms include symptoms similar to heart failure. Diastolic dysfunction means that your heart does not fill properly.
The left atrium may also increase in size due to. These results can change from echo to echo depending on the underlying condition. In fact its estimated that more than 50 of adults of over the age of 70 have diastolic dysfunction.
Grade 3 and 4. It is evaluated on a scale of 1 - IV with I being the mildest and IV being the most severe. Grade II diastolic dysfunction is called pseudonormal filling dynamics.
End-diastolic volume index at 20 mmHg EDVi20 in patients stratified according to diastolic function grade. Diastolic dysfunction is a significant cause of pulmonary hypertension increased blood pressure in the lung. The most common cause is that the walls of the left ventricle have become thickened and not able to relax and the most common cause of that is high blood pressure over a long period of years.
In most patients left atrial and left ventricular end-diastolic filling pressures are elevated the left atrium is increased in size and patients often complain of exertional dyspnea. These patients more than likely have symptoms of heart failure. This is a moderate condition that shows elevated left atrial filling pressures.
Aging is the most common cause of this stiffening of the heart. This is a moderate condition that shows elevated left atrial filling pressures. As I mentioned there are still readers basing their diagnosis of diastolic dysfunction or impaired relaxation on information from.

Criteria Used To Define The Grade Of Diastolic Dysfunction Download Table

Diastolic Dysfunction Dr S Venkatesan Md

Diastolic Heart Failure Ppt Video Online Download
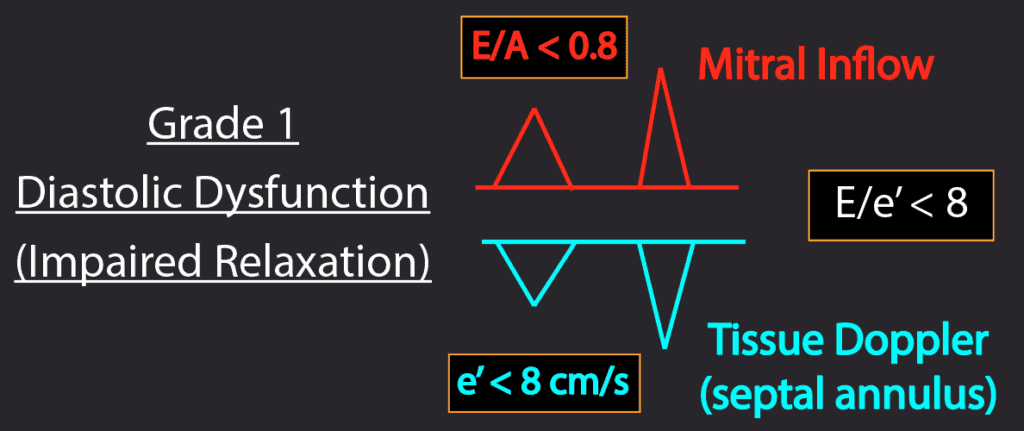
How To Measure And Grade Diastolic Dysfunction Using Echocardiography Pocus 101

5 Steps To Identify Diastolic Dysfunction In Echo

Impact Of Progression Of Diastolic Dysfunction On Mortality In Patients With Normal Ejection Fraction Circulation

Echocardiographic Evaluation Of Diastolic Function Can Be Used To Guide Clinical Care Circulation

Grading For Diastolic Dysfunction Dd According To American Society Of Download Table

Grades Of Diastolic Dysfunction Download Table
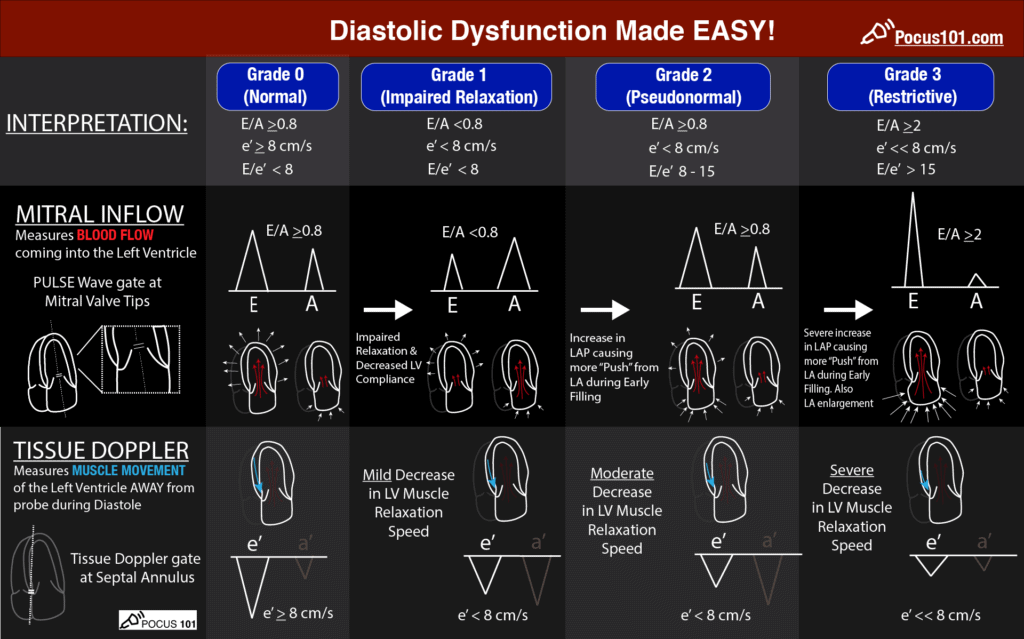
How To Measure And Grade Diastolic Dysfunction Using Echocardiography Pocus 101

Congestive Heart Failure Diastolic Topic Review Learntheheart Com

Diagnosis And Management Of Diastolic Dysfunction And Heart Failure American Family Physician

Utility Of A Simple Algorithm To Grade Diastolic Dysfunction And Predict Outcome After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery

Diastolic Function Diastolic Dysfunction 123 Sonography

Diastolic Function Diastolic Dysfunction 123 Sonography

Practical Approach To Grade Diastolic Dysfunction By Echocardiography Download Scientific Diagram

Diastolic Dysfunction Part Ii Grading Ase 2016 Youtube

